


What is a GST invoice? GST Invoicing is essential for registered dealers within the goods and services tax framework. It serves as a formal statement of goods or services exchanged. The GST invoice details the transaction and facilitates the correct application of CGST and SGST while ensuring compliance and transparency in the taxation process. Let’s understand this invoice in detail.
Table of Contents
A GST invoice is a comprehensive transaction record between sellers and buyers. It details the services or products provided and the total amount payable.
The GST tax invoice further offers structure and clarity to customers. It allows them to monitor their payments and applicable deductions effectively.
Under GST, sellers have legal obligations to issue invoices, particularly when the total transaction value exceeds ₹200. To ensure compliance with the legal framework, sellers should promptly generate invoices upon confirmation of the order. A GST invoice offers clarity to the customers and facilitates effortless tracking of payments, thereby promoting transparency and accountability in the transactions.
The GST invoice is also essential for businesses to claim Input Tax Credits. It helps them reduce tax liability by offsetting input tax against output tax. For invoices under ₹2 lakh, signatures from both seller and customer are mandatory, confirming transaction details and agreed amounts. This documentation is vital as it precedes payment, ensuring sale particulars are transparently and traceably recorded.
The GST system in India utilises various invoices to accommodate different types of transactions and scenarios. Understanding these invoices is crucial for businesses to ensure compliance with GST rules and to facilitate accurate tax filing.
This invoice is issued by a registered entity when supplying goods or services exempt from GST. It is also used when the supplier is registered under the Composition Scheme. Unlike a regular tax invoice, this invoice does not contain GST. A registered entity may issue an invoice-cum-bill of supply when taxable and exempt supplies are made to an unregistered customer.
An Aggregate Invoice consolidates multiple sales of goods or services made to the same customer, typically when the value of each invoice does not exceed a specified limit. This simplifies the process of invoicing under GST and reduces paperwork. Aggregation can occur when the transactions are uniform and occur within the same state.
It is issued by a registered entity when the taxable value of a supply needs to be reduced or when goods are returned. It serves as a correction to the original tax invoice. It is necessary when the taxable value or tax levied in the invoice exceeds the taxable value or tax payable regarding such supply.
A Debit Note or Supplementary Invoice is issued to increase the taxable value of the goods or services supplied or to account for post-sale price adjustments. This could be because of a price revision or a mistake in the original invoice. The issuance of this invoice is necessary when the taxable value or tax charged in the invoice is less than the taxable value or tax payable.
The Reverse Charge Invoice is issued when the tax liability shifts from the supplier to the registered recipient of goods or services under the reverse charge mechanism. This invoice must include specific details such as the nature of the supply, the tax payable, and the reason for the reverse charge. The GST regulations govern the timelines for issuing a Reverse Charge Invoice.
A GST invoice must have the following details:
If your recipient is not registered under GST and the invoice value exceeds ₹50,000, then the invoice should include the following details as well:
You can use Razorpay Invoices to create and send GST-compliant invoices to your customers and accept payments instantly. You can create, update, cancel and delete invoices from your dashboard. These GST invoices can also be saved as templates for your future reference.
If you’re wondering how to include profit margins and to get real-time GST inclusive and exclusive rates you can check out our free GST calculator.
Explore the essential elements required for a comprehensive GST invoice. Below are visual representations of illustrating GST invoice formats.
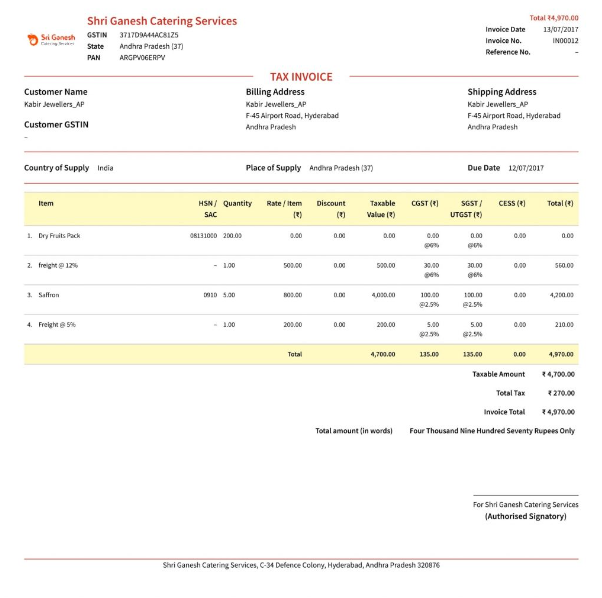 How to Create a GST Invoice?
How to Create a GST Invoice? GST invoice contains all the details of the supply of goods or services and applicable GST taxes and discounts. Creation of GST invoices can be done manually or through computer software.
Numerous accounting software programs are available which have an in-built invoice-generation facility. Once you enter the sales/ outward supply and all relevant details, an invoice is automatically generated, printed, and issued to the buyer.
Following are the basic steps to understand how to make GST bill. No matter what kind of software anyone uses, these steps are more or less the same.
Choose the relevant branch (out of multiple branches) that will issue the GST invoice. If there is no branch, this option will not appear.
Type in the Invoice Date. One can also set the date of payment if outward supply is made on a credit basis. If payment is received on the same date, then the invoice date and the payment date will be the same.
The list of customers/debtors is to be fed in before you create an invoice. The drop-down tab will show all these debtors. Select the relevant customer. If you haven’t fed in customer data, one can easily use the option, ‘Create Debtor/Customer.’
Place of supply is an essential requirement to ascertain the GST tax type: ‘IGST or CGST & SGST.’ The place of supply will be self-selected according to the delivery/shipment address. If such address is not known, the place of supply will be deemed to be the State where such supplier is registered.
From the drop-down tab, simply select the goods or services which are to be supplied. If such a list is not previously typed-in, one can simply select ‘Create Item’ and type in the relevant details of goods/services.
CGST tax rate will auto-populate (based on the universal HSN/SAC codes generally in-built in software). Then select unit, quantity, any discount/incentives. IGST or CGST & SGST for the selected goods/services will be automatically shown.
If all the above details are given, simply click the ‘Create GST Invoice’ option. Such an invoice is downloadable (either in Excel or pdf format) and can be printed.
One can also create an invoice using this online facility: Razorpay Invoices.
Important Note: The above steps are for the creation of ‘GST Tax Invoice’ meant for Regular Taxpayers. For Composition Taxpayers, ‘Bill of Supply’ is created for which the above steps are equally applicable. The only difference: GST Tax cannot be charged in a Bill of Supply. The Tax Invoice and Bill of Supply have been explained below.
You can also calculate the due tax breakup of GST using Razorpay’s Online GST calculator based on different tax slabs.
You can instantly validate a GSTIN using our free GST Number Search & Verification Tool, which helps you verify the authenticity of a GST number online.
Now that you know how to make a GST bill online, understand a few common mistakes to avoid.
Ensure all mandatory GST invoice fields are filled out accurately. This includes the GSTIN, invoice number, date, recipient details, and itemised details of goods or services provided.
Always verify the supplier and recipient’s GST Identification Number (GSTIN). Incorrect GSTINs can lead to issues with input tax credits.
Maintain a sequential and unique invoice numbering system. Mismatched or duplicate invoice numbers can cause confusion and compliance issues.
The invoice date should align with the supply date to avoid discrepancies affecting tax liability and reporting.
To ensure accurate tax classification, use each item’s correct Harmonised System of Nomenclature (HSN) or Service Accounting Code (SAC).
Double-check all calculations, including taxable amounts, GST rates, and total amounts, to prevent inaccuracies in tax calculations.
Mention if the invoice is subject to the reverse charge mechanism in GST. Omitting this can lead to compliance issues.
Maintain a consistent and standardised format for all invoices to ensure clarity and ease of understanding.
State the place of supply on the invoice, as it determines the applicable GST rates. Failure to do so can contribute to incorrect tax calculations.
Different transactions require different types of invoices, such as a tax invoice or a bill of supply. Based on the nature of the transaction, issue the correct type.
Adhere to the timelines for GST return filing and issuing invoices. Late actions can result in penalties and affect the recipient’s input tax credit.
Stay informed about the latest GST rules and regulations. Non-compliance can lead to penalties, legal issues, and loss of input tax credit.
Issuing a GST invoice is a critical aspect of the tax compliance process for businesses. As said before, it serves as documented proof of the supply of goods or services and is essential for the supplier and the recipient to claim input tax credit.
However, suppliers may encounter complexities due to the diverse nature of transactions and the specific requirements for different types of supplies. The government provides comprehensive guidelines to overcome these challenges and ensure suppliers understand when and how to issue a GST invoice correctly.
Here are some more insights:
As per Section 2(96) of the CGST Act, suppliers must generate an invoice on or before the removal of goods for supply. The term ‘removal’ can be interpreted in two ways: when the goods are dispatched for delivery or when the recipient collects them.
The law provides flexibility in invoice issuance in a continuous supply of goods where there is a recurring business relationship. Suppliers should issue invoices before the account statement is created or payment is received, whichever is earlier.
For services, the GST law mandates that invoices be issued within 30 days of the service’s completion. This strict timeframe is crucial for complying with GST regulations and enables service recipients to claim input tax credits timely.
Banks and Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) have a unique timeline for issuing GST invoices. Unlike other service providers, they have a 45-day window to issue GST receipts, reflecting the distinct nature of financial services and their transaction cycles.
Although the issuance of an invoice is essential, there are specific conditions under which the issuance of a GST tax invoice is not mandatory.
It is crucial to note that both conditions must be met simultaneously for the exemption to apply. The supplier must still issue a tax invoice if only one condition is met.
An alternative method is available for registered suppliers who meet these conditions. They can issue a consolidated tax invoice at the end of each day for all the supplies made to unregistered recipients who did not require an invoice.
This approach is permissible under the GST legal framework and is designed to simplify the invoicing process for small-value transactions.
However, suppliers must strictly adhere to the specified conditions to avoid any legal complications. Failure to comply with the GST invoicing rules can result in penalties and affect the supplier’s eligibility for ITC claims.
Revising invoices is crucial for maintaining accurate tax records in the GST regime’s dynamic landscape. Dealers must be well-versed in the procedures for revising invoices, as this directly impacts their financial reporting and tax liabilities.
Under GST, dealers must obtain provisional registration and subsequently convert it to a permanent registration certificate. Once they have received their GST registration certificate, they will have a specific timeframe for issuing revised invoices. This period is typically within one month from the issuance date of the registration certificate.
According to Rule 53 of the Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Act, 2017, revisions can include upward or downward price adjustments and alterations in GST rates. These revisions can be made to correct errors or to reflect changes in the transaction value or tax amount.
A revised GST invoice must comprise the following particulars:
When issuing a revised GST invoice, it is essential to mark the document as ‘Revised Invoice’ where applicable. This helps distinguish it from the original invoice and ensures clarity during audits or assessments.
Including a unique and consecutive serial number on the revised invoice is of paramount importance because it helps track the invoice and ensures that each invoice is easily identifiable.
In the context of goods supply under the GST system, it is mandatory to issue three essential copies of the invoice:
Each copy plays a crucial role in the logistics and documentation processes, ensuring transparency and accountability in the movement of goods and the claiming of ITC.
For the supply of services, the invoicing process is more streamlined, involving only two key copies:
The nature of service transactions does not necessitate additional copies since there is no physical movement of goods that requires tracking or verification by multiple parties.
In conclusion, the GST (Goods and Services Tax) invoice serves as a vital document in the modern taxation system, facilitating transparency, efficiency, and compliance. Through standardized formats and stringent regulations, it streamlines the process of tax collection and ensures accuracy in reporting transactions. Moreover, the GST invoice not only acts as proof of purchase but also enables businesses to claim input tax credits, thereby reducing the cascading effect of taxes. Overall, its implementation marks a significant step towards simplifying the tax structure, promoting ease of doing business, and fostering economic growth.
Businesses registered under GST in India must issue a GST invoice for sales. A delivery challan is used instead if no sale occurs, but goods move. Non-registered entities or transactions exempt from GST can issue invoices without GST details .
Yes, the GST invoice can be handwritten as long as it is legible and contains all the required details.
Yes, mentioning HSN or SAC codes on a GST invoice is mandatory in India. For businesses with turnover above ₹5 crore, 6-digit codes are required. For those below, 4-digit codes for goods and services suffice.
To check a GST invoice’s validity in India, verify the GSTIN on the invoice using the GST portal’s ‘Search Taxpayer’ option. Input the GSTIN; a valid entry will display the taxpayer’s details, while an invalid one will prompt an error message.
You can track GST invoices for ITC through Form GSTR-1/IFF and view them in Form GSTR-2B.
Yes, you can use invoicing software to generate GST-compliant invoices in India.
GST invoices should be issued within 30 days of the service supply. Regular businesses with over ₹5 crore turnover can file two monthly and one annual return. Small taxpayers under the QRMP scheme file quarterly returns and pay taxes monthly.
Corrections to an already-issued GST invoice can be made through a revised or supplementary invoice. For significant changes, issue a credit or debit note. Ensure all amendments comply with GST regulations and are reported in the monthly returns.
To cancel a GST invoice in India, log into the GST portal, navigate to the ‘e-Invoice’ section, and select ‘Cancel e-Invoice’. Enter the invoice reference number (IRN), choose a cancellation reason, add remarks if necessary, and submit. The cancellation must comply with the GST regulations.
Yes, non-compliance with GST invoicing rules can result in penalties. For not issuing an invoice, the penalty is 100% of the tax due or ₹10,000, whichever is higher and a penalty of ₹25,000 for incorrect invoicing. Specific offences may attract different penalties.